
- #DOCKER FOR MAC KUBERNETES MOUNT LOCAL VOLUME HOW TO#
- #DOCKER FOR MAC KUBERNETES MOUNT LOCAL VOLUME DRIVER#
Suppose that you want to share some files with multiple docker containers. Sharing a Docker Volume with multiple Docker Containers In order to delete all the volumes at once, you need to make sure that none of the volumes is currently in use and then use the following command. After you have stopped the container, you can use the following command to remove the volume. If a container is running with the volume mounted in it, you would have to stop the container first before removing the mounted volume. In order to delete a docker volume, you need to ensure that the volume is not in use at that moment. You can verify this by going to the specified location inside the container.

This would open an ubuntu bash with the volume mounted in the specified location. The command for this is sudo docker run −−mount source=,destination= įor example, if you want to mount a volume called myVolume to an ubuntu container at a location /usr/src/app/ inside the container, you can do so using the following command − sudo docker run −it −−mount source=myVolume,destination=/usr/src/app/ ubuntu You can also mount the same volume to multiple Docker containers and all the containers would have a shared access to the volume. You can easily mount a Docker Volume to a Docker container using the -mount flag when you are running the Docker run command. The command for inspecting a Docker volume is − sudo docker volume inspect
#DOCKER FOR MAC KUBERNETES MOUNT LOCAL VOLUME DRIVER#
It would list all the details regarding the Docker volume which would include the date of creation, mountpoint, driver name, name of the volume, etc. To inspect a particular Docker volume, you can use the Docker inspect command. Once you run the above command, a list will be displayed which would contain the driver name and the volume name of all the existing volumes. Now that you have created a docker volume, if you want to list all the existing Docker volumes, you can do so using the following command. The command for creating a Docker volume is − sudo docker volume create įor example, if you want to create a volume with the name myVolume, you can do so using the following command.

This directory is located in the path /var/lib/docker/volume. On executing the command, Docker creates a particular directory for volume on the local machine. You can create a Docker volume using the create command.
#DOCKER FOR MAC KUBERNETES MOUNT LOCAL VOLUME HOW TO#
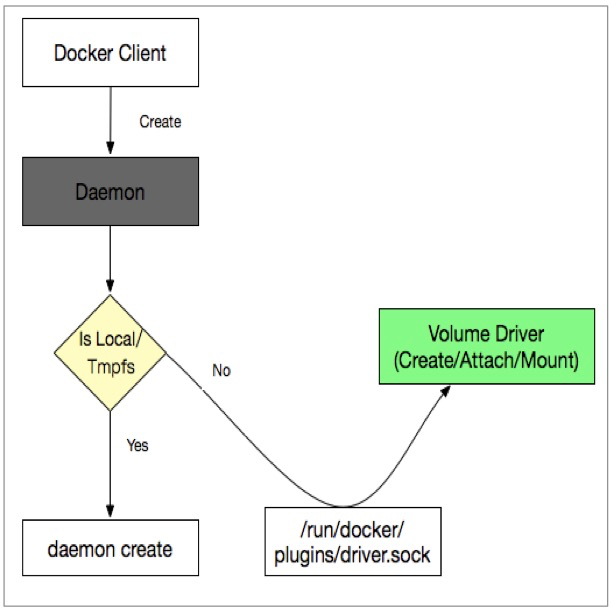
In this article, we are going to discuss how to create, list, inspect, mount and delete docker volumes with the help of commands. It is also possible to mount the same volume to different containers and this allows easy sharing of data between them and this can be easily achieved with the use of simple commands and flags. We can easily mount a volume when we launch a Docker container. One of the major advantages of Docker Volumes is that it allows the developers to backup their data and also allows easy sharing of file systems among Docker containers. They help in preserving the data and are independent of the container life cycle. To define Docker Volumes, they are file systems that can be mounted on Docker containers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
